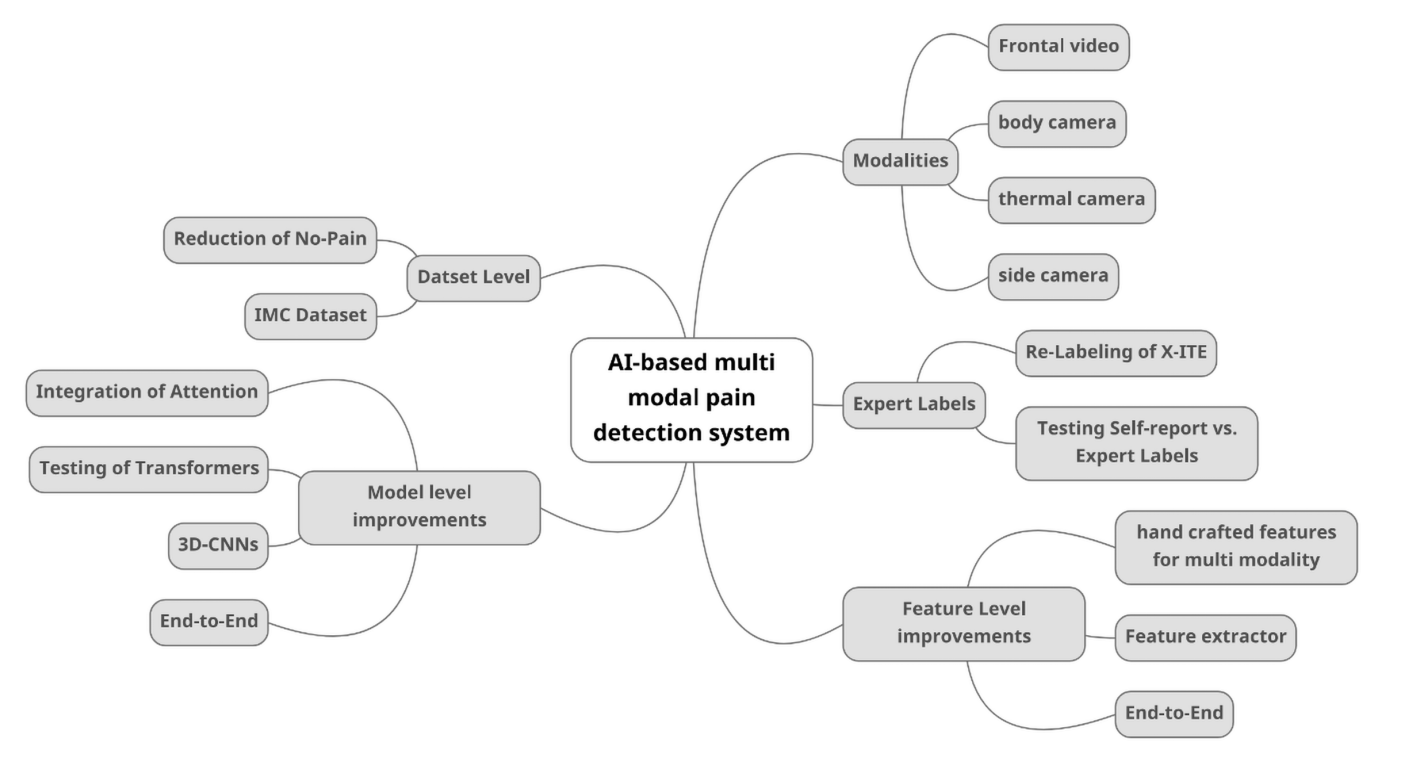
Multi modal AI based pain detection
Development of a robust, reliable and multimodal AI system for the pain quantification
Motivation
Previous research conducted by the NIT working group has led to significant advancements and AI-based methods in the field of pain detection. However, recent developments in machine learning, particularly the use of attention mechanisms in foundation models, offer further improvements in both the accuracy and robustness of such systems. Additionally, since pain databases like BioVid and X-ITE rely on self-reported pain as ground truth, the resulting AI models may not be applicable to patients who are unable to communicate or self-report. Therefore, it is necessary to construct a secondary ground truth for the X-ITE database, based entirely on expert assessments of perceived pain through observed pain expressions.
Goals
The aim of this project is to develop a robust and reliable pain detection system. This will be achieved by building on previous findings from the NIT research group, which remain state-of-the-art in the field of pain detection. New machine learning technologies will be applied to these findings using the BioVid and X-ITE databases, and the resulting models will be evaluated against current state-of-the-art approaches. Furthermore, an extensive study will compare the model performance based on self-reported pain labels versus the newly created expert-labeled ground truth in the X-ITE database. Combined with real-world data from the postoperative IMC project, these efforts are expected to result in a highly robust and generalizable pain detection system.