DFG
SEMIAC
Home
Implicit mobile human-robot communication for spatial action coordination with action-specific semantic environment modelling
With the increasing use of robots in industrial and everyday contexts, the need for systems that can interact flexibly and cooperatively with humans is growing. Collaborative robots (cobots) in particular, which share a common workspace with humans and can react to complex, dynamic environments, are coming into focus. A central challenge here is the context-related perception of the environment and the appropriate interpretation of human behavior.
Founding
The project SEMIAC - Implicit mobile human-robot communication for spatial action coordination with action-specific semantic environment modelling (Implizite mobile Mensch-Roboter-Kommunikation für die räumliche Handlungskoordination mit aktionsspezifischer semantischer Umgebungsmodellierung) is funded by the German Research Foundation (DFG) under grant No. 502483052 and is planned with a project duration of 3 years (2023 to 2026).
Publications

Automated 3D Dataset Generation for Arbitrary Objects
October 06, 2025

Scene-Aware Prediction of Diverse Human Movement Goals
October 01, 2025

Learning Human–Robot Proxemics Models from Experimental Data
September 18, 2025

Robot System Assistant (RoSA) evaluation of touch and speech input modalities for on-site HRI and telerobotics
June 30, 2025
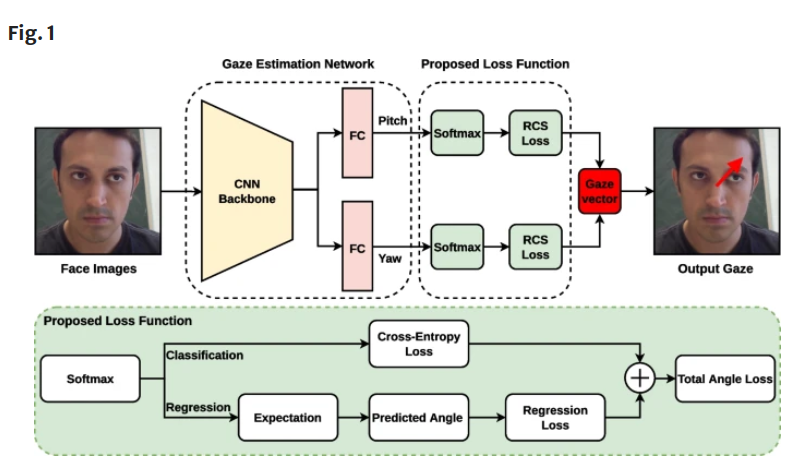
Multi-Head Attention-Based Framework with Residual Network for Human Action Recognition
May 06, 2025
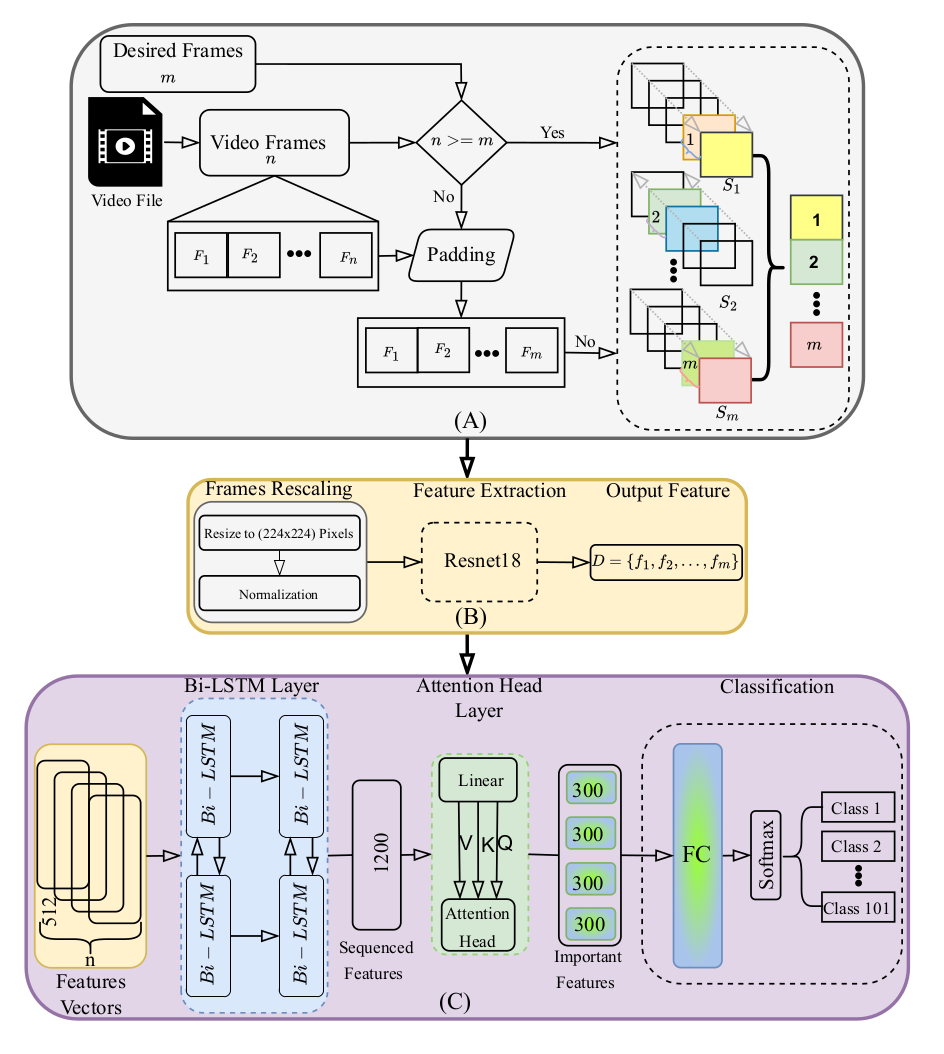
IM HERE – Interaction Model for Human Effort based Robot Engagement
April 29, 2025

Automating 3D Dataset Generation with Neural Radiance Fields
April 29, 2025
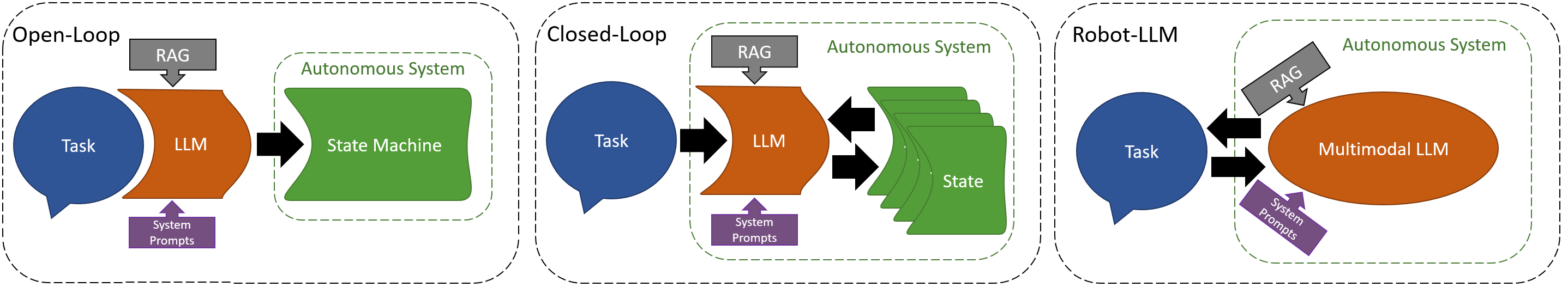
Toward Truly Intelligent Autonomous Systems A Taxonomy of LLM Integration for Everyday Automation
April 28, 2025
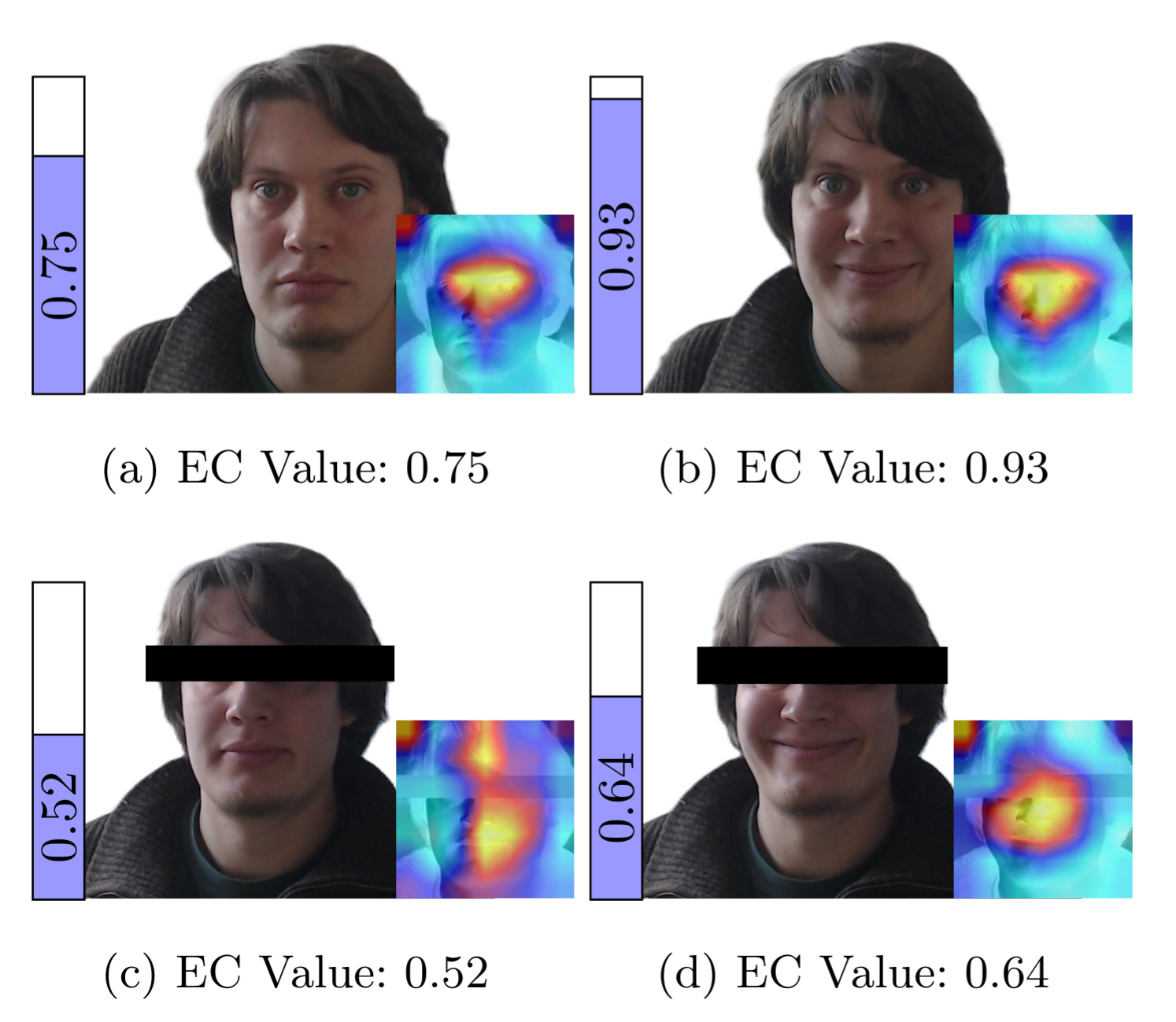
Eye Contact Based Engagement Prediction for Efficient Human-Robot Interaction
April 28, 2025
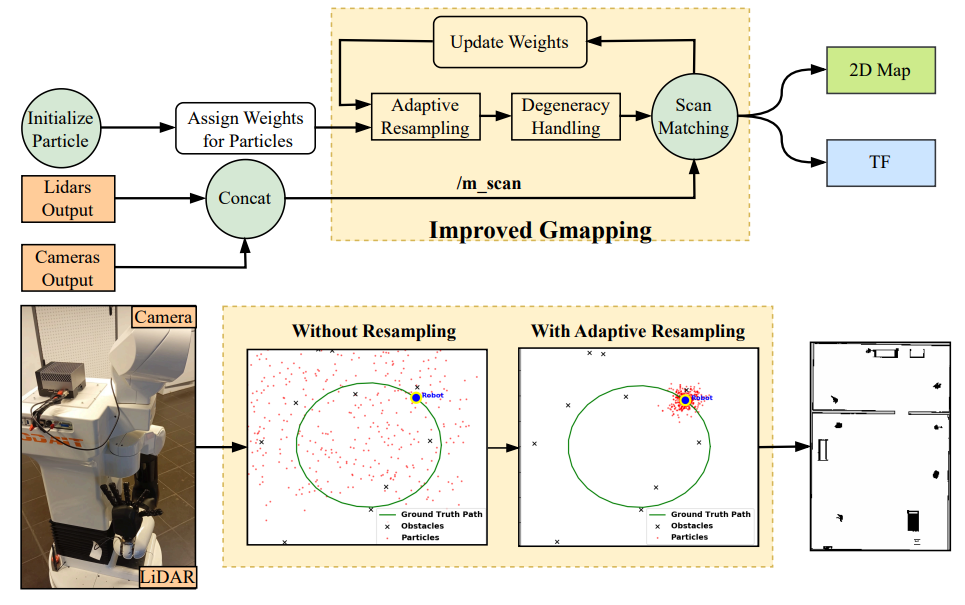
Mobile Robot Navigation with Enhanced 2D Mapping and Multi-Sensor Fusion
April 10, 2025